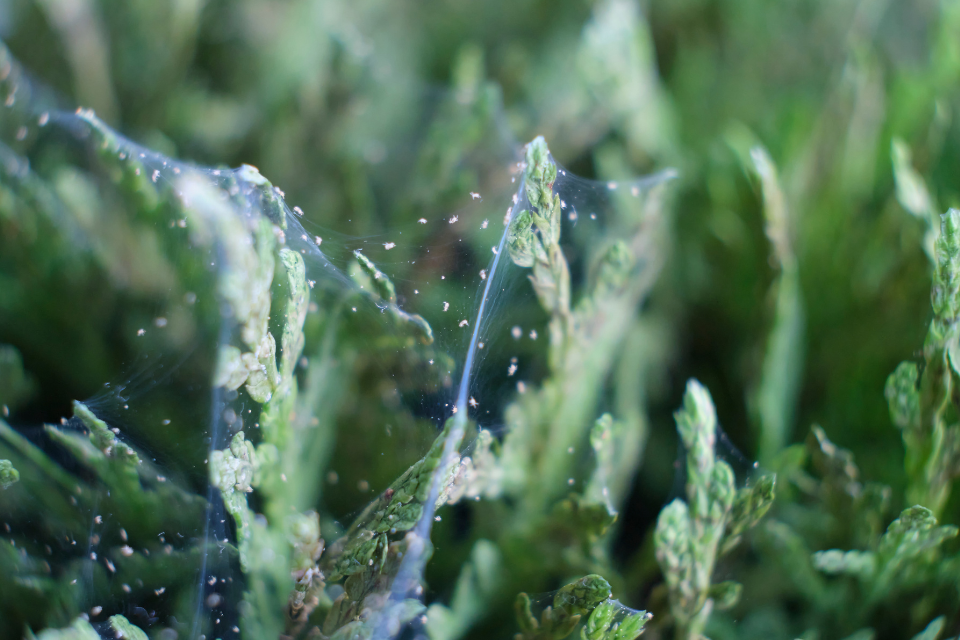
What Are White Spots on Plant Leaves & How to Treat Them
Noticing white spots on plant leaves can be concerning, as these seemingly minor specks often indicate underlying issues that could seriously threaten your plants’ health if not addressed promptly. These spots may be caused by various factors, ranging from fungal infections to environmental stress.
Understanding the exact cause and the right treatment is crucial for preventing further damage. This article provides a detailed guide to understanding the possible causes of white spots on plant leaves, along with effective treatments to help protect your plants and keep them thriving. Read on to discover what’s troubling your plants.
Common Causes of White Spots on Plant Leaves
cultivated plants require specific conditions to flourish, including correct lighting, sufficient nutrients, and so on. If these conditions aren’t met, your plants can become vulnerable to various issues. White spots on leaves of plants can result from one or more factors. Understanding the causes of these spots is essential for finding the right treatments. The following are the common causes:
Fungal Disease
A wet and humid environment makes plants prone to fungal infections. The most notorious fungus responsible for white spots is powdery mildew, but several other fungi can cause similar problems.
Powdery mildew: This fungus is a common cause of white spots on leaves, easily identifiable by a white, powdery substance that coats the leaves. The spots tend to spread quickly if not treated and can affect both indoor and outdoor plants. Powdery mildew thrives in humid environments, often appearing in shaded areas with poor air circulation.
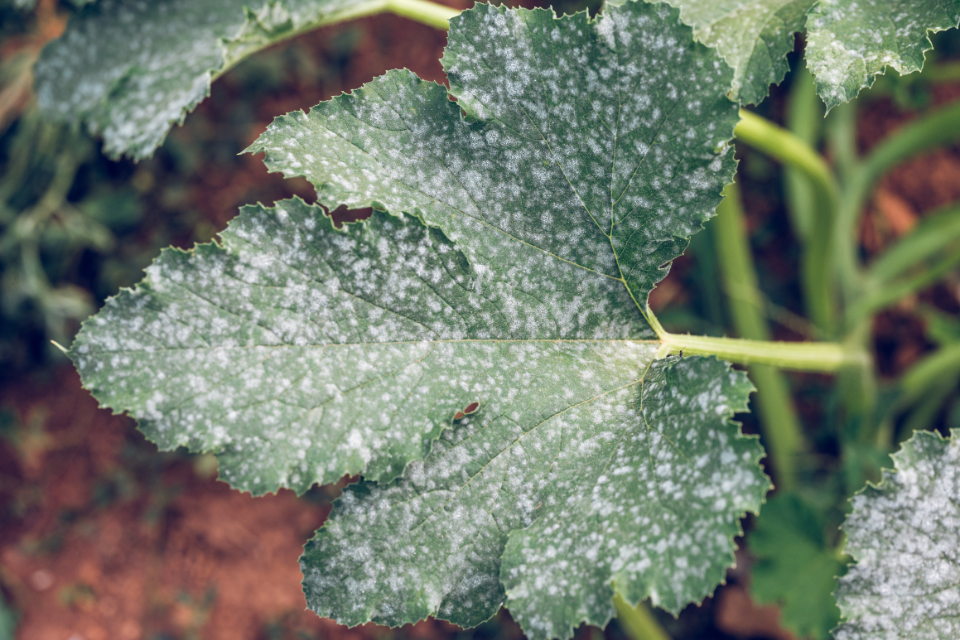

Downy mildew: Downy mildew is another prevalent fungal disease that leaves white spots on plant leaves, especially on vegetables like cauliflower, broccoli, squash, and cabbage. Downy mildew thrives in cool, damp, and crowded environments where leaves remain moist and dense for extended periods.
Late Blight: Late blight, caused by the Phytophthora infestans pathogen. It primarily affects Solanaceae family plants, including potatoes, tomatoes, eggplants, and peppers. This highly contagious disease can destroy plants within days, with symptoms such as rotting leaves with white spots and stems that develop dark blotches.
Insects & Pests
Several pests can cause white spots on plant leaves. As these pests infest and feed on the leaves, they often leave behind white, brown, or yellow spots. The most common pests include:
Spider mites: The symptoms of spider mites infection are tiny white or yellow spots with fine webbing on the undersides of leaves.
Leafminer: Leafminers eat the cells of the tomato leaves as they go which will leave a squiggly line of dead, whiteish tissue behind.
Mealybugs: Mealybugs are the bane of any houseplant owner’s existence. Mealybugs and tiny, white insects that cluster together in cottony masses on leaves—especially areas of new growth.
Aphids: This kind of small, soft-bodied insects that suck plant sap, causing white or yellowish spots on leaves.
Whiteflies: These tiny, winged insects are covered in a white, waxy powder. They resemble small white spots and cluster on the underside of leaves.
Scale Insects: These pests form large clusters during feeding, shedding cottony skins that leave white remnants on the plant.
Nutritional Deficiency
All living organisms need essential nutrients to thrive and develop properly. It’s crucial to closely monitor for nutrient deficiencies. A lack of certain nutrients can lead to discoloration, including whitening.
Nitrogen Deficiency: Nitrogen is a crucial element for plant growth. A deficiency typically causes older leaves to turn yellow, starting from the tips and progressing inward. Affected leaves may become pale and exhibit overall poor growth.
Calcium Deficiency: A calcium deficiency can cause white or pale spots, especially on new leaves, as it affects cell structure.
Magnesium Deficiency: Insufficient magnesium may result in interveinal chlorosis, leading to white or yellowish spots between the veins of older leaves.
Sun Scald
Plants need light, whether natural sunlight or artificial light to grow and stay healthy. However, intense sunlight can lead to sunscald, especially if plants are suddenly exposed to bright light after periods of cloud cover or shade. Sunscalds appear as white or brown spots on the leaves.
Salt Build-Up
Salt build-up can occur when the water used for your plants is too hard or contains excessive nutrients. This build-up manifests as white spots on the leaves, which are generally harmless. However, if you notice that these affected leaves are becoming brittle and developing brown edges, it may signal a more serious issue.
How to Get Rid of White Spots on Plant Leaves
As discussed, several factors can lead to white spots on plant leaves. Identifying the root cause is key to applying the right solution and addressing the issue effectively. In the sections that follow, we’ll provide targeted solutions for each cause mentioned earlier. Let’s dive in!
Treatment of Fungal Disease
Pruning: For plants with minimal infection, you can just cut off the diseased leaves with scissors and throw them out. However, if the disease has spread to the stalks, the entire plant should be dug out and destroyed to prevent further spread.
Chemical fungicides: Chemical fungicides are widely used to combat fungal infections. Common active ingredients include copper-based fungicides-effective for treating diseases such as powdery mildew, downy mildew, and blights, Sulfur-based fungicides- against a broad spectrum of fungal diseases, and so on.
Baking Soda: Mix 1 tablespoon of baking soda, a few drops of liquid soap, and a gallon of water, then spray the solution onto the affected leaves.
Potassium Bicarbonate: Combine 1 tablespoon of potassium bicarbonate with a gallon of water and spray it onto the affected leaves.
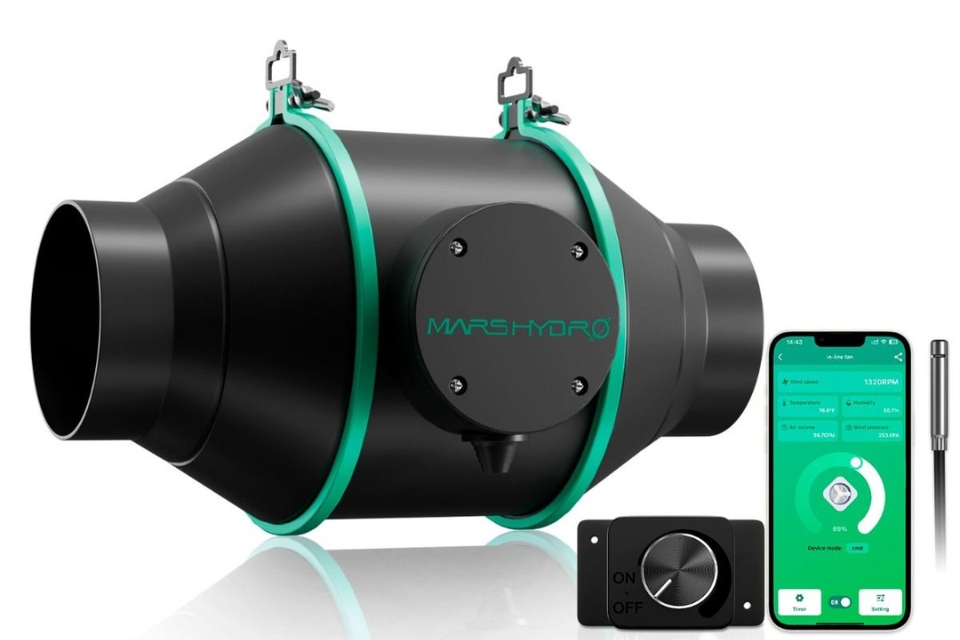
Improve Air Circulation: Space plants adequately to ensure good airflow. For indoor gardens, like those in grow tents, consider using an inline fan to boost air circulation.
Mars Hydro inline duct fans assist in regulating humidity by exhausting stale air containing excess moisture and bringing in fresh, drier air. This prevents the development of mold and mildew, which thrive in humid conditions.
Treatment of Pests
Insecticidal soaps are an excellent solution for managing a wide range of pests, including aphids, spider mites, and whiteflies. These soaps work by disrupting the pest’s cell membranes, leading to dehydration and death. For best results, apply the soap according to the label instructions, ensuring thorough coverage of both the tops and undersides of the leaves, where pests often hide.
In addition to using insecticidal soaps, it’s important to establish a routine of daily plant inspections. Early detection of pests allows for timely intervention before infestations become severe. Look for signs such as discolored or damaged leaves, small webs, or tiny crawling insects. If you spot early signs of infestation, act immediately to prevent the pests from spreading.
Treatment of Nutritional Deficiency
First, use a soil tester to analyze the soil and identify any nutrient deficiencies. This allows you to apply nutrients in a targeted and efficient manner, ensuring your plants receive exactly what they need for optimal growth.
If your soil lacks nitrogen, then you can enhance plant development by adding nitrogen-rich materials like horn meal or composted manure. These organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly, ensuring a steady supply of nitrogen to promote lush, healthy foliage.
Kelp meal, a nutrient-dense organic amendment, provides essential micronutrients such as calcium, magnesium, iodine, manganese, and molybdenum. These elements are key for supporting overall plant health, boosting stress tolerance, and enhancing disease resistance in plants.
Treatment of Sun Scald
If you’re growing plants outdoors, you can install shade netting to protect them from intense sunlight. Shade netting helps regulate the amount of sunlight your plants receive, preventing sunburn and reducing heat stress, especially during the hottest parts of the day.
For indoor growers, If the light is too strong, you can either switch to a lower-wattage grow light or upgrade your traditional grow light to LED grow lights, which produce less heat. This ensures that your plants receive the appropriate amount of light without being overexposed, promoting healthy growth and preventing light stress.
Treatment of Salt Build-up
Watering the soil deeply and slowly helps flush out excess salts, preventing salt buildup around plant roots. This method ensures salts are leached past the root zone and don’t affect nutrient uptake. For best results, use rainwater or distilled water, as these are free from salts and impurities found in tap water.
If you’re growing in containers, raised planters with proper drainage are ideal for avoiding waterlogging and salt accumulation. Good drainage helps excess water and salts escape more efficiently, preventing them from concentrating in the root zone.
Conclusion
White spots on plant leaves can signal various issues, but with accurate identification and appropriate treatment, you can effectively address most problems and keep your plants thriving. Whether the spots are caused by pests, diseases, or nutrient deficiencies, prompt action is key to restoring plant health and ensuring continued productivity.
If you’re still confused about the white spots on plant leaves after these, don’t hesitate to leave a comment below.